
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) prevails as one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In light of this pressing global concern, researchers of the Leibniz Research Alliance INFECTIONS have now added another puzzle piece to the bigger picture of AMR. Their study, published in Frontiers in Microbiology, sheds light on the intricate interplay of factors contributing to the proliferation of AMR in animal farming.

Join us for this innovative summer school on Antimicrobial Resistance: Navigating Between Access & Excess. Dive into interdisciplinary discussions, cutting-edge research, and innovative strategies to combat one of the greatest health challenges of our time. From economic implications to environmental impacts, from policy perspectives to scientific breakthroughs – this immersive program offers a unique opportunity for PhD students and postdocs across diverse research fields to shape the future of global health. Don't miss your chance to be part of this transformative journey!
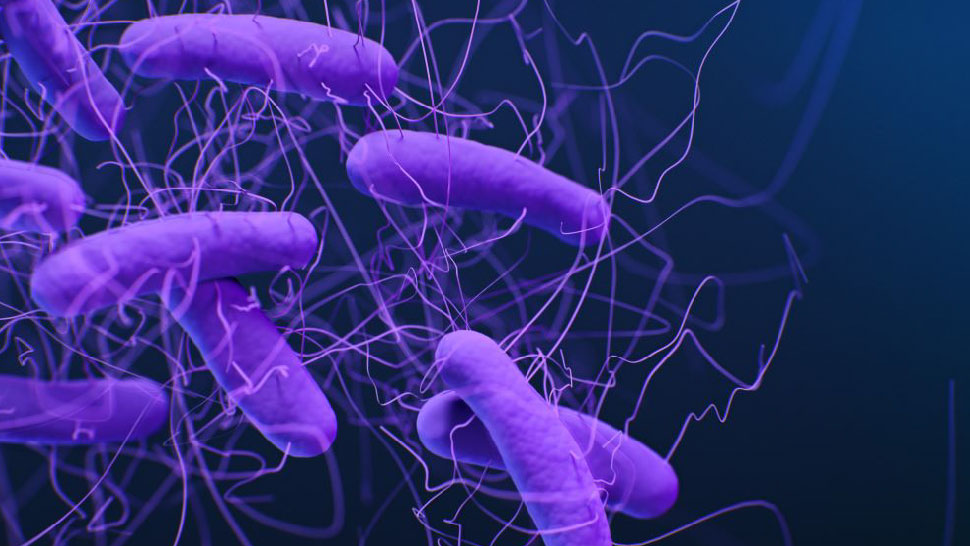
Clostridioides difficile is a bacterium that occurs worldwide in the intestines of humans and animals. If the composition of the intestinal flora is out of balance, e.g. due to the intake of medication, these pathogens can become rampant. The toxins excreted by the bacteria then lead to sometimes severe intestinal inflammation, which can be fatal.
The inflammation is usually treated by administering an antibiotic that is effective against C. difficile. Three different antibiotics are currently recommended for this treatment: vancomycin, fidaxomicin or metronidazole (the latter in exceptional cases). In the last 25 years, however, the frequency of mutations has increased, which leads to a decreased susceptibility to these drugs and thus reduces the success of the therapy.

The new Leibniz Lab "Pandemic Preparedness: One Health, One Future" links excellent inter- and transdisciplinary research from 41 Leibniz institutes. For the first time in Germany, pathogen-oriented sciences (virology, bacteriology, mycology and immunology) are collaborating with other life sciences such as ecology, health technologies, health economics and educational research. This new instrument of the Leibniz Association will be funded for three years with three million euro. The aim of the Leibniz Lab is to pool research in these areas in order to prepare, to prevent and to respond better to future pandemics and to make the knowledge gained available to policymakers in the form of evidence-based recommendations for action.

At the beginning of February, the symposium "Long-term Consequences of Infections" of the Leibniz Center Infection (LCI) research network in northern Germany took place in Hamburg with over 120 participants. The Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine, the Borstel Research Center, the Leibniz Lung Center and the Leibniz Institute of Virology - all partner institutes of LFV INFECTIONS - founded this alliance in 2005 in order to strengthen infection research in the Hamburg metropolitan region in the long term.
Press Release Leibniz Center Infection